INS in the Peripheral Nervous System
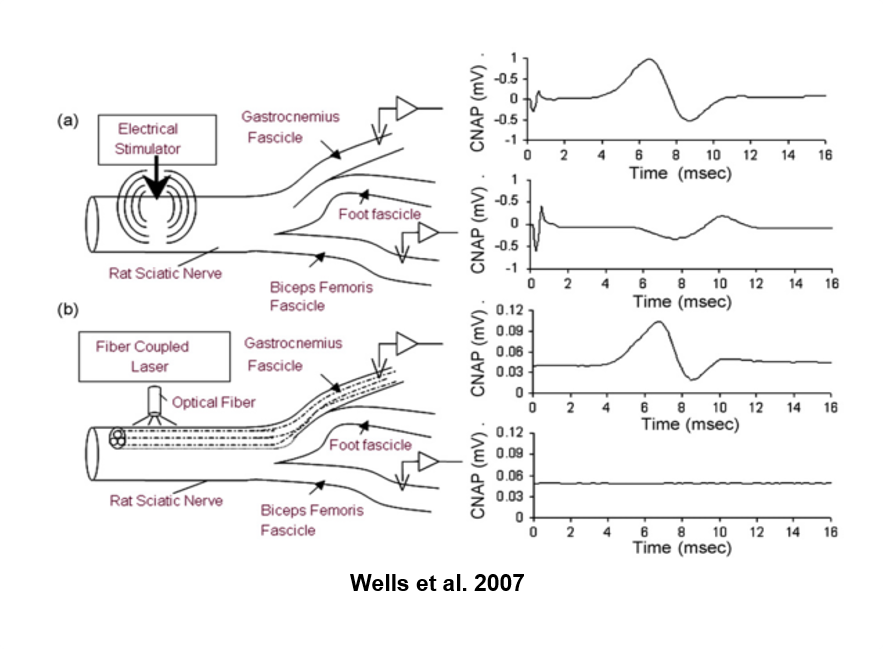
Our lab was first showed in 2005 that short single pulses of strongly-absorbing infrared (IR) light can be used to precisely and accurately excite neural activity in the peripheral nervous system. Operating without genetic modification or exogenous substance applications, at the sacrifice of genetic and biochemical specificity, makes pulsed infrared light a promising technology for improving clinical nerve identification and neural mapping technologies. We also believe that pulsed IR neuromodulation could be useful for neuroscience research, where genetic alteration and photochemical uncaging approaches are not practical. We have shown safe and effective applications of INS in the peripheral and central nervous system of slugs, frogs, rats, nonhuman primates, and humans. One area of our lab focuses on translating INS technologies for intraoperative use, specifically in medical device design and development, early stage clinical applications towards high resolution neural mapping, nerve identification, and nerve regeneration.
The contact and artifact free high spatial precision IR stimulation can be advantageous in certain clinical situations, such as mapping of nerves during tumor resection or providing better frequency encoding in cochlea implants. With these applications in mind, our group has performed the first study to apply INS in humans. In patients undergoing selective dorsal root rhizotomy, we have shown that INS can activate dorsal roots with better spatial precision than electrical stimulation. No artifact was generated from INS and stimulation could be achieved in a contact free method. The results of this study have established the efficacy needed to start additional clinical trials to improve upon current standard of care where electrical stimulation has proven to be inadequate.
We are also pursuing neuro-regenerative applications using INS. Nerve damage is a difficult problem to combat due to the fact that neuronal healing and cell division does not readily occur. Regenerative medicine research has advance drastically over the last couple of decades to restore motor function to damaged nerves, though often accompanied by a reduced ability to sense through damaged nerves following regeneration. One area of our lab focuses applying INS to facilitate proprioceptive nerve regeneration to restore sensing abilities in damaged nerves rat models of nerve regeneration.
Researchers
Faculty
Graduate Students
Publications
Cayce, J. M. et al. Infrared neural stimulation of human spinal nerve roots in vivo. Neurophotonics 2, 015007 (2015).
M. W. Jenkins, A. R. Duke, GuS, DoughmanY, H. J. Chiel, FujiokaH, WatanabeM, E. D. Jansen, and A. M. Rollins, "Optical pacing of the embryonic heart," Nat Photon, vol. 4, pp. 623-626, 2010.
A. D. Izzo, J. T. Walsh, Jr., H. Ralph, J. Webb, M. Bendett, J. Wells, and C. P. Richter, "Laser stimulation of auditory neurons: effect of shorter pulse duration and penetration depth," Biophys J, vol. 94, pp. 3159-66, Apr 15 2008.
Wells, J. D. et al. Optically mediated nerve stimulation: Identification of injury thresholds. Lasers Surg. Med. (2007).
J. D. Wells, S. Thomsen, P. Whitaker, E. D. Jansen, C. C. Kao, P. E. Konrad, and A. Mahadevan-Jansen, "Optically mediated nerve stimulation: Identification of injury thresholds," Lasers Surg Med, vol. 39, pp. 513-26, Jul 2007.
J. D. Wells, C. Kao, P. E. Konrad, T. Milner, J. Kim, A. Mahadevan-Jansen, and E. D. Jansen, "Biophysical mechanisms of transient optical stimulation of peripheral nerve," Biophys J, vol. 93, pp. 2567–2580, May 25 2007.
J. Wells, P. Konrad, C. Kao, E. D. Jansen, and A. Mahadevan-Jansen, "Pulsed laser versus electrical energy for peripheral nerve stimulation," J Neurosci Methods, vol. 163, pp. 326-37, Jul 30 2007.
A. D. Izzo, J. Joseph T. Walsh, E. D. Jansen, M. Bendett, J. Webb, H. Ralph, and C.-P. Richter, "Optical parameter variability in laser nerve stimulation: a study of pulse duration, repetition rate, and wavelength," IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. 54, pp. 1108-1114, 2007.
A. D. Izzo, C.-P. Richter, E. D. Jansen, and J. T. Walsh, "Laser stimulation of the auditory nerve," Laser Surg Med, vol. 38, pp. 745-753, 2006.
Wells, J., Kao, C., Jansen, E. D., Konrad, P. & Mahadevan-Jansen, A. Application of infrared light for in vivo neural stimulation. J. Biomed. Opt. 10, 064003 (2005).
J. D. Wells, C. Kao, K. Mariappan, J. Albea, E. D. Jansen, P. Konrad, and A. Mahadevan-Jansen, "Optical stimulation of neural tissue in vivo," Optics Lett, vol. 30, pp. 504-506, 2005.
J. D. Wells, C. Kao, E. D. Jansen, P. Konrad, and A. Mahadevan-Jansen, "Application of infrared light for in vivo neural stimulation," J Biomed Opt, vol. 10, p. 064003, 2005.
 Our lab was first showed in 2005 that short single pulses of strongly-absorbing infrared (IR) light can be used to precisely and accurately excite neural activity in the peripheral nervous system. Operating without genetic modification or exogenous substance applications, at the sacrifice of genetic and biochemical specificity, makes pulsed infrared light a promising technology for improving clinical nerve identification and neural mapping technologies. We also believe that pulsed IR neuromodulation could be useful for neuroscience research, where genetic alteration and photochemical uncaging approaches are not practical. We have shown safe and effective applications of INS in the peripheral and central nervous system of slugs, frogs, rats, nonhuman primates, and humans. One area of our lab focuses on translating INS technologies for intraoperative use, specifically in medical device design and development, early stage clinical applications towards high resolution neural mapping, nerve identification, and nerve regeneration.
Our lab was first showed in 2005 that short single pulses of strongly-absorbing infrared (IR) light can be used to precisely and accurately excite neural activity in the peripheral nervous system. Operating without genetic modification or exogenous substance applications, at the sacrifice of genetic and biochemical specificity, makes pulsed infrared light a promising technology for improving clinical nerve identification and neural mapping technologies. We also believe that pulsed IR neuromodulation could be useful for neuroscience research, where genetic alteration and photochemical uncaging approaches are not practical. We have shown safe and effective applications of INS in the peripheral and central nervous system of slugs, frogs, rats, nonhuman primates, and humans. One area of our lab focuses on translating INS technologies for intraoperative use, specifically in medical device design and development, early stage clinical applications towards high resolution neural mapping, nerve identification, and nerve regeneration.