CHEMISTRY 102A Fall, 1999
HOUR EXAM #2
NAME (Please Print) _______________________________________________________________
Name of your Professor ____________
Lecture Section _______ ( List-1, Ekman-2, Hall-3, Phillips-4 )
School (A&S, Eng., Other) ________
I pledge on my honor that I have neither given nor received improper aid on this examination.
_______________________________________________
Signature
You will have exactly two hours to complete your exam.
Before you begin, CAREFULLY READ AND FOLLOW THE INSTRUCTIONS BELOW.
Instructions
- Check to see that your exam contains all seven pages.
- Show all work neatly and completely to receive partial credit.
- Write your answers clearly and legibly. Answers not clearly written will be marked wrong.
- Include units with answers.
- Direct any questions to the supervising instructor or graduate student proctors.
Equations and constants
- g = 9.807 m/s2
- R = .08206 Latm/molK
- R = 8.314 J/mol
- R = 8.314 kgm2/s2molK
- 1 u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg
- avg. KE = (3/2)RT
- urms = (3RT/molar mass)1/2
- (P + a(n/V)2)(V nb) = nRT
I. True/False check the appropriate blank (2 points each 10 points total)
|
True |
False |
1. Real gases deviate from ideal gas behavior at both low temperatures and low pressures.
|
________ |
________ |
|
2. The process of reduction must always accompany the process of oxidation..
|
________ |
________ |
|
3. When comparing two liquids, the substance with the higher vapor pressure will have the lowest normal boiling point.
|
________ |
________ |
|
4. As a gas escapes a vessel, the temperature of the gas decreases if the pressure and volume inside the vessel are kept constant.
|
________ |
________ |
|
5. Intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces) are weaker than covalent bonds.
|
________ |
________ |
II. Select the one best match for the following terms. (2 points each 14 points total)
| 1. Ion-dipole interaction |
________ |
| 2. The oxidation number of Br in HBrO4 |
________ |
3. CH3COOH is an example of a
|
________ |
|
4. Dispersion forces
|
________ |
|
5. The oxidation number of C in C2H4O2
|
________ |
|
6. KOH is an example of a
|
________ |
|
7. The oxidation number of H in CaH2
|
________ |
| A) Strong acid |
G) -1 |
M) +8 |
| B) Weak acid |
H) 0 |
N) The attraction between the permanent dipole moments of polar molecules. |
| C) Strong base |
I) +1 |
P) The attraction between instantaneous charge separations in electron clouds due to electron movement. |
| D) Weak base |
J) +2 |
Q) The attraction most responsible for the dissociation of salts into ions in aqueous solution. |
| E) Base anhydride |
K) +4 |
R) The repulsions between molecules that keep the molecules as widely separated as possible. |
| F) Acid anhydride |
L) +7 |
S) The attraction caused when an ion induces a dipole moment in a non-polar molecule. |
III. Multiple choice. For the following questions pick the best possible answer
(5 points each, 25 points total). If you circle two answers, one of which is correct, you will receive 2 points.
- The spectator ions in the following reaction are?
Al(OH)3 (s) + 3 HNO3 (aq) à Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 H2O (l)
- Al3+, NO3-
- H+, NO3-
- H+
- NO3-
- none of the above
- The UF6 molecule is approximately 175 times more massive than molecular hydrogen. Both substances are gases at 500 K. If 0.001 moles of each gas were confined in separate 10 L containers at 500 K the pressure of the UF6 would be?
- much greater than the H2 pressure.
- much less than the H2 pressure.
- the same as the H2 pressure.
- exactly 5 times greater.
- not enough information given to determine the answer
- Which of the following statements about strong acids is true?
- All strong acids have H atoms bonded to electronegative O atoms.
- Strong acids are completely (100%) ionized in water.
- Strong acids are very concentrated acids.
- Strong acids are oxidized during reactions with bases.
- All of the above.
- The formula for hydrobromic acid is
- HBr
- H2Br
- HBrO3
- HBrO4
- none of the above
- Which of the following is an example of a redox reaction?
- 3 Na2S (aq) + Fe2(SO4)3 (aq) à 3 Na2SO4 (aq) + Fe2S3 (s)
- 2 Mn+3 (aq) + 2 H2O (l) à Mn+2 (aq) + MnO2 (s) + 4 H+ (aq)
- P2O5 (s) + 3 H2O (l)à 2 H3PO4 (aq)
- H2SO4 (aq) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) à CaSO4 (aq) + 2 H2O (l)
- none of the above
IV. Short answer / fill in the blank.
1. (10 pts total) Phosphorous forms trihalides with each of the halogens. At room temperature one is a gas, two are liquids and one is a solid.
- (2 pts) Which of the phosphorous trihalides (PF3, PCl3, PBr3, PI3) is the solid?
- (4 pts) What are the two types of intermolecular forces that exist for the phosphorous trihalides? (Be specific)
- (4 pts) In three sentences or less explain why the trihalide you predicted to be a solid is a solid and the other trihalides are not solids.
2. (6 pts) Refer to the generic phase diagram below. Label the diagram indicating the phases, special curves and points.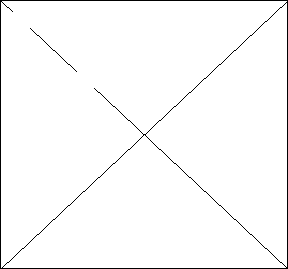
- ____________________
- ____________________
- ____________________
- ____________________
- ____________________
- ____________________
3. (6 pts) For the following reactions write the NET ionic reaction. Write NR in box if no reaction takes place.
- Sodium hydroxide reacting with copper (II) chloride in water.
- Ammonium sulfate reacting with barium chloride in water.
V. Problems. Put final answer in box. Show your work for full credit.
1. (6 pts) Airbags are inflated with nitrogen gas produced by the decomposition of sodium azide shown below. How much sodium azide is needed to fill an air bag with a volume of 40.0 L to a pressure of 1.20 atm at a temperature of 25.0 °C?
2 NaN3 (s) à 2 Na (l) + 3 N2 (g)
2. (6 pts) A solution of potassium dichromate can be used to dissolve cadmium metal, according to the following equation. How many milliliters of 1.20 M K2Cr2O7 are required to react with exactly 6.00 g of Cd?
K2Cr2O7 (aq) + 14 H+ (aq) + 3 Cd (s) à 2 Cr3+ (aq) + 7 H2O (l) + 3 Cd2+ (aq) + 2 K+ (aq)
3. (6 pts total) A mixture of gases is found to contain Ar, Kr, and Ne. The partial pressure of Ar was found to be 200. torr, Kr = 300. torr and Ne = 125. torr.
- (1 pt) What is the total pressure of the mixture of gases?
- (2 pts) What is the mole fraction of Kr?
- (3 pts) If the gas mixture remains confined to a constant volume while the absolute temperature changes from 300. K to 500. K, what is the new total pressure?
4. (6 pts) A 60.0 mL volume of gas is found to have a pressure of 1.02 atm at a temperature of 20.0 °C while having a mass of 0.101 g. What is the molar mass of the gas?
5. (5 pts) A sample of methane containing 12CH4 and 13CH4 is to be separated by gaseous diffusion. What is the enrichment factor? (Assume the relative atomic masses are 12C = 12.00 u, 1H = 1.00 u, and 13C = 13.00 u)
