Physics Demo Number: 158
Approximate
Run Time: 5 min
Brewster's Angle By Laser Reflection From a Plastic Block
Demo Description
Linear polarization of a reflected beam of light is achieved by bouncing a 5 mW laser beam off of a plastic block.
Scientific Principles
-
Light reflected off a dielectric surface is partially polarized by the reflection.
-
At a particular angle of reflection one finds the polarization to be 100%.
Equipment
-
Plastic block and a plate of polarizing material
-
5 mW Demonstration Laser
Equipment Location
-
Kit (158) {Shared with Kit(108)} on [C-4-4]
-
Laser on [C-2-4]
Instructions
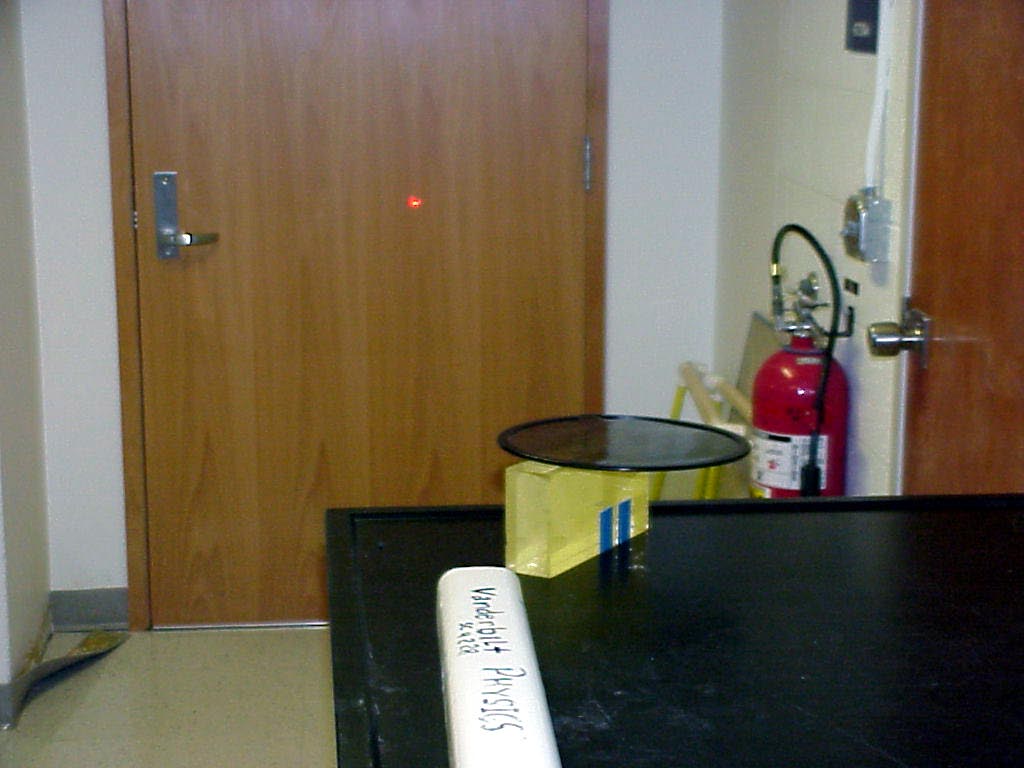

The
5mw HeNe laser is seen shining straight ahead onto the door in the
first photo. Use of the round Polaroid filter seen resting on top
of the plastic block shows the laser light to be unpolarized.
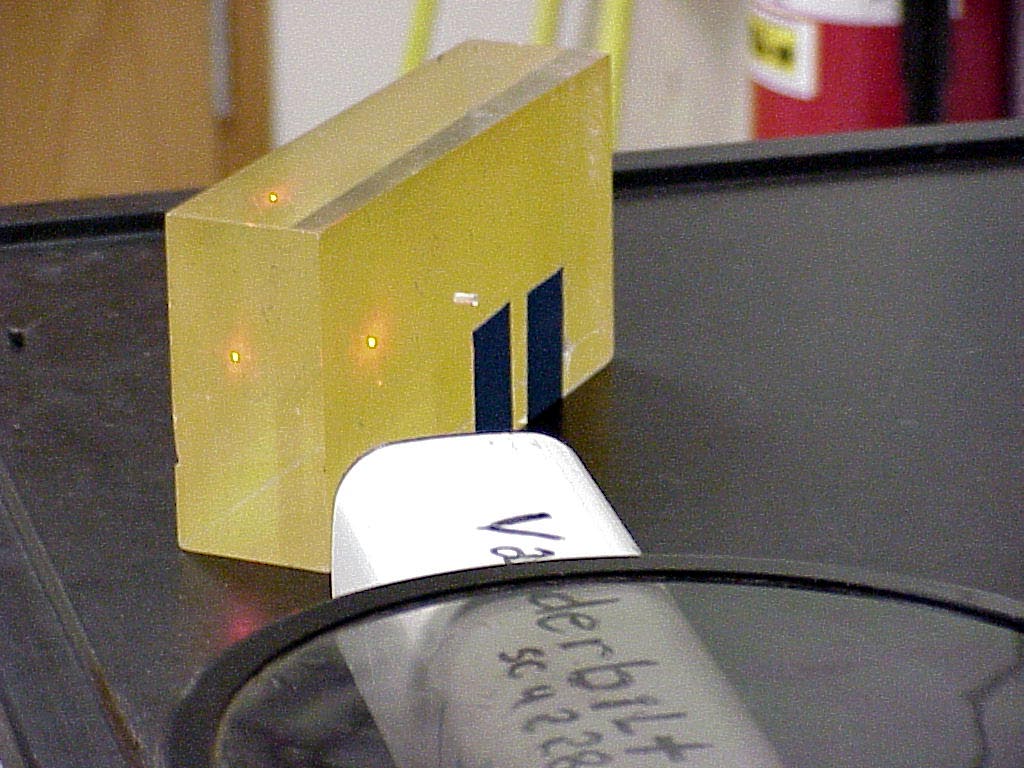
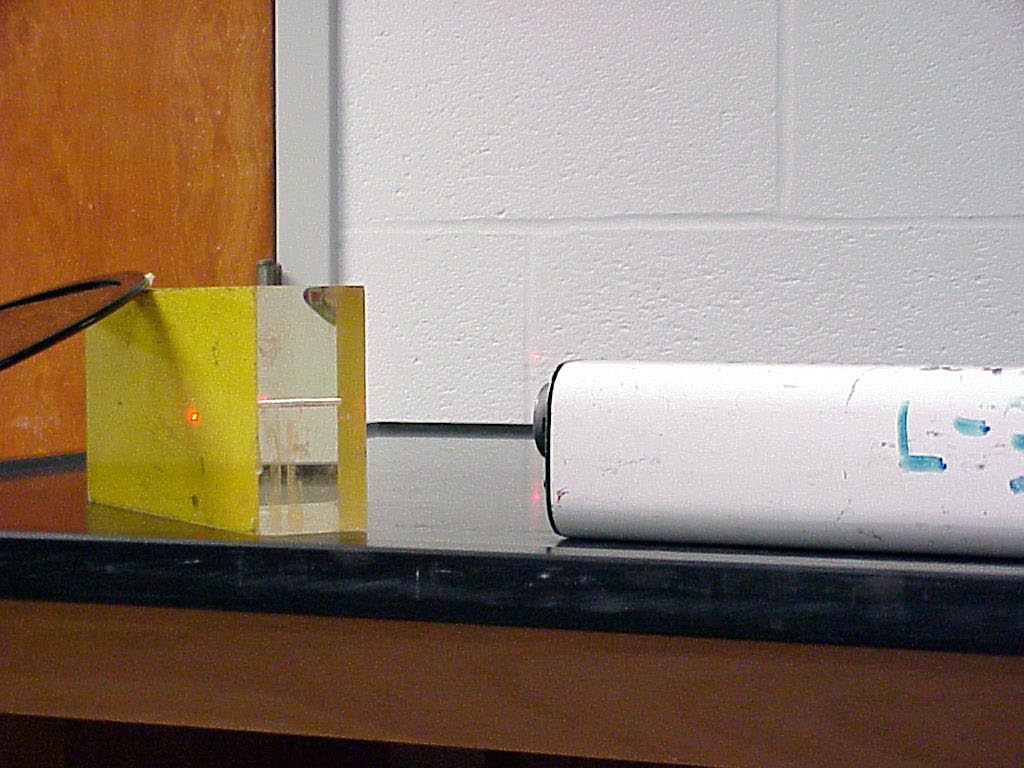
One now slides the block over to intercept the laser beam on the front face of the block. This results in a reflected beam angling over to the wall behind the table on the right in the photo. The second photo shows this state of affairs, for the laser beam striking the block,

while
the third photo shows the beam on the right hand wall.
If
the filter is placed in the beam, either before reflection or
after reflection, it can be noted that the reflected beam is
partially polarized. Adjustment of the reflection angle by
rotating the block will lead to nearly total polarization of the
reflected beam. The angle for which total polarization occurs is
known as Brewster's Angle.
Writeup created by David A. Burba
Copyright © 2013, Vanderbilt University. All Rights Reserved.